Scientific report 2023 of the Lymphoma Working Party (LWP)

Major achievements
In 2023 the LWP was able to improve its performance in the most important field of CART therapy.
Two projects – TransCART (CART and allo SCT in 3L treatment of LBCL) and CART in r/r LBCL with CNS involvement – were selected by the GoCART Coalition for funding as high priority projects. The results of the TransCART were presented at the 49th Annual Meeting of the EBMT in April 2023. IPI at the time of cell therapy was established as an important prognostic tool. CART therapy is especially effective in patients with r/r LBCL and limited adverse prognostic factors. In high-risk r/r LBCL is still a mostly unmet medical need as the relapse incidence (RI) of CART is high (> 60%). Due to its high anti-lymphoma activity but high toxicity allogeneic SCT remains a valuable therapeutic modality e.g. after CART failure.
We performed a retrospective RWE study in patients with r/r LBCL and CNS involvement. With an PFS of 30% and OS of 52% at one year, we could demonstrate that CART in this clinical situation is as effective as in patients without CNS involvement. The results compare favourably to those obtained with other clinical modalities obtained in the same clinical situation. The CART-CNS project was an oral presentation at ASH 2023. A manuscript is preparation.
A third CART related project compared the results of CART treatment with brexucabtagene autoleucel (brexu-cel) in r/r mantle cell lymphoma within the clinical phase II study ZUMA-2 with allogeneic SCT in comparable clinical situation treated by allogeneic SCT registered in the EBMT registry. Brexu-cel was superior in terms of OS (81.3% vs 59.2 % @ 1year) and showed a significantly lower NRM (7.1 vs 21,2 % at 1 year) compared to allogeneic SCT. However, there was no significant difference in PFS and ongoing relapses were seen after brexu-cel whilst the incidence of relapse after two years was every low after allogeneic SCT.
To give a benchmark for further clinical studies and retrospective analysis, we analysed the outcome of autologous and allogeneic SCT in DLBCL. It could show continuously better results for autologous SCT over time but decreasing use with the upcoming CART therapy.
Another group of studies focuses on Hodgkin's lymphoma and the embedding of cellular therapy onto complex treatment algorithms with other modern non-cellular therapies. A joint EBMT / CIBMTR analysis showed that prior use of checkpoint inhibitors significantly improves the results of subsequent allogeneic SCT substantially and may establish a new stand of care for advanced r/r HL.
Ongoing projects focus on the role of CPI and Brentuximab vedotin prior and after autologous SCT.
Another retrospective analysis compared the results of haploidentical versus MUD (8/8 HLA match) allogeneic SCT in lymphomas using post-transplant cyclophosphamide as GVHD prophylaxis. In contrast to the results found e.g. in acute leukaemia, MUD was superior to haploidentical SCT in terms of OS and PFS mostly due to lower incidence of severe GVHD and NRM.
In fields in which the success of new agents is missing, analysis of classical allogeneic and autologous SCT remains of major importance for clinical decision-making. One of these fields is treatment of T cell lymphoma. We started a couple of analysis on the role of allogeneic and autologous SCT in T-NHL and other rare diseases. With the largest cohort of patients analysed so far, we could show that allogeneic stem cell transplantation is of high efficacy. With a 3 years PFS and OS of 48.6% and 55.6% and no relapses beyond 3 years allogeneic SCT was confirmed to be standard of care in r/r NK/T cell lymphoma with curative potential.
Principal research studies
Key publications
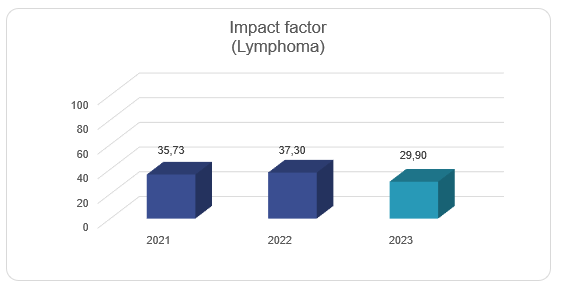
| 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oral presentations | 1 | 2 | 10 |
| Poster presentations | 0 | 3 | 5 |
| Educational events | 1 | 1 | 1 |